Knowledge base article
Optimising Wordfence firewall and security settings
This guide recommends the best configurations to optimise Wordfence firewall and security settings for WordPress
Wordfence is a powerful firewall and security plugin offering a range of protection settings to strengthen WordPress application security and resilience against web attacks.
To enhance the protection Wordfence offers, we've compiled our recommended Wordfence configuration settings which are verified by our WordPress Management team as highly beneficial.
Note: This guide recommends configurations for the free version of WordPress so no premium Wordfence features will be referenced.
Let's begin!
- Login to WordPress and navigate to the Wordfence dashboard. If you've not yet installed Wordfence, you can download Wordfence free on WordPress.org.
- Select All Options on the left hand side tool bar, then navigate to the Brute Force Protection section and set the following parameters:
Enable brute force protection >> ON
Lock out after how many login failures >> 5
Lock out after how many forgot password attempts >> 5
Count failures over what time period >> 2 hours
Amount of time a user is locked out >> 5 days
Prevent the use of passwords leaked in data breaches >> Enabled For all users with "publish posts" capability.
Leave the remaining default settings in this section as is.
To assist implementing these recommendations, you can also reference the following visual representation of the settings: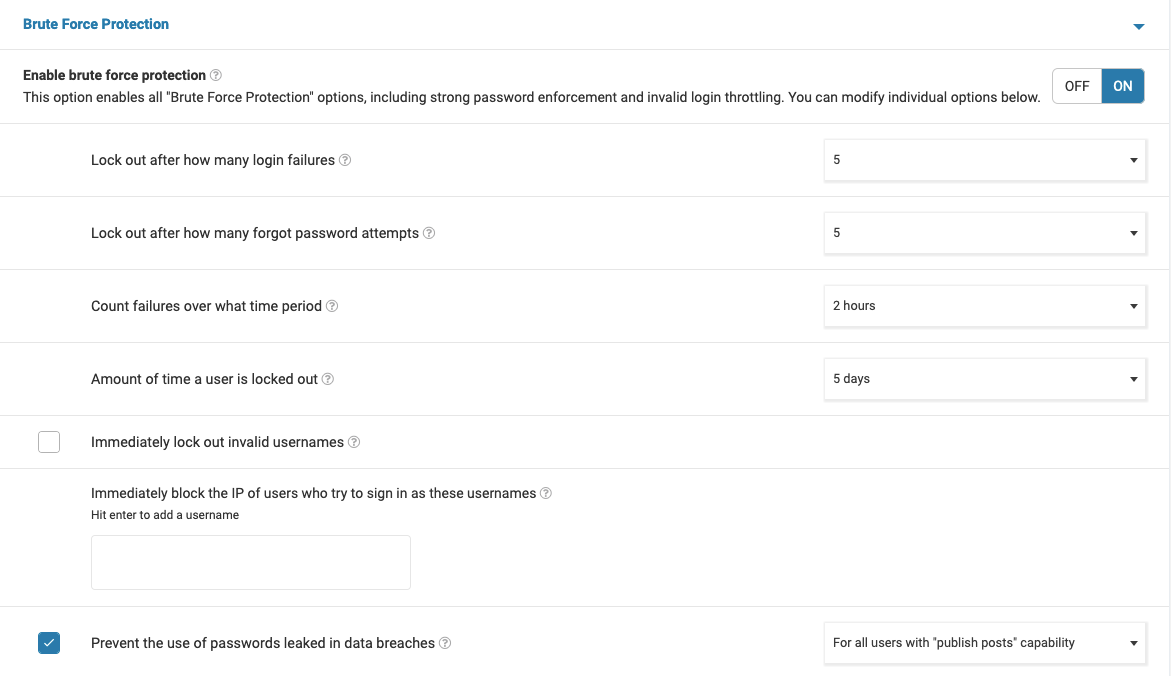
- Scroll down to the next section labelled Rate Limiting and set the following parameters:
Enable Rate Limiting and Advanced Blocking >> ON
How should we treat Google's crawlers >> Treat Google like any other Crawler
If anyone's requests exceed >> 240 per minute then throttle it
If a crawler's page views exceed >> 240 per minute then throttle it
If a crawler's pages not found (404s) exceed >> 240 per minute then throttle it
If a human's page views exceed >> 240 per minute then throttle it
If a human's pages not found (404s) exceed >> 240 per minute then throttle it
How long is an IP address blocked when it breaks a rule >> 1 day
You can also reference the following visual representation of the settings: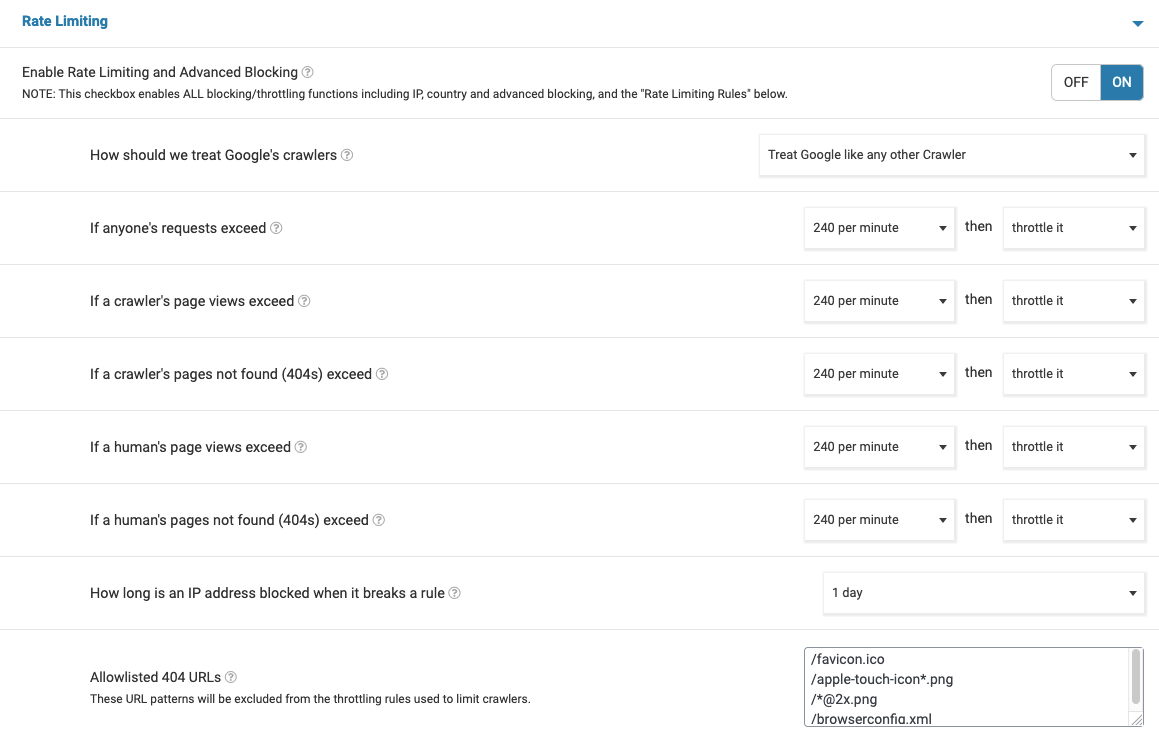
- Select SAVE CHANGES.
These recommendations are curated after hands on experience with hundreds of WordPress applications however these settings are always best tailored to your needs so adjust the settings as necessary.
Published June 21, 2022. Last updated November 30, 2023.
Can't find what you're looking for?
"*" indicates required fields